Kidney stone disease
(Redirected from Urolithiasis)
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Author:
Mikael Häggström [notes 1]
Kidney stone disease, also known as urolithiasis, is when a calculus (kidney stone) occurs in the urinary tract.[1]
Contents
Acute disease - planning
Need for imaging
Imaging is indicated in cases of flank pain and hematuria.[2]
Choice of modality
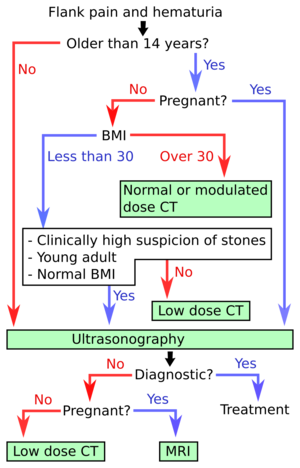
Algorithm for kidney stone disease, developed in the US.[3]
- Ultrasonography of kidney stone disease is the first-line imaging modality for patients <14 years of age and those who are pregnant. It is also the first-line investigation for thin (BMI <30) patients and there is a strong suspicion of kidney stone disease.[2] In the algorithm at right, hydronephrosis may count as a diagnostic finding of urolithiasis.
- CT of kidney stone disease is recommended for older patients, as well as those who have higher BMI and/or less specific findings.[2]
Recurrent
See CT in recurrent kidney stone disease.
Notes
- ↑ For a full list of contributors, see article history. Creators of images are attributed at the image description pages, seen by clicking on the images. See Radlines:Authorship for details.
References
- ↑ . Kidney Stones in Adults (February 2013). Archived from the original on 11 May 2015. Retrieved on 22 May 2015.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Brisbane, Wayne; Bailey, Michael R.; Sorensen, Mathew D. (2016). "An overview of kidney stone imaging techniques ". Nature Reviews Urology 13 (11): 654–662. doi:. ISSN 1759-4812.
- ↑ Brisbane, Wayne; Bailey, Michael R.; Sorensen, Mathew D. (2016). "An overview of kidney stone imaging techniques ". Nature Reviews Urology 13 (11): 654–662. doi:. ISSN 1759-4812.